光学超构表面原理与应用
光学超构表面一类由介质或金属超构单元以二维阵列排布构成的用于控制光的偏振、相位和振幅等自由度的新型人工光学平台。在过去的十年中,超构表面的概念被广泛用于研发各类光学功能器件,例如超构透镜、超构全息和超构非线性光源等。

鉴于光学超构表面在成像、波前工程、非线性光学、量子信息处理等方面的丰富应用前景,在主编杨兰教授和副主编Yuri Kivshar院士的支持下,Photonics Research推出了Optical Metasurfaces: Fundamentals and Applications专题,由南方科技大学的李贵新教授、德国耶拿大学的Thomas Pertsch教授、哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)的肖淑敏教授和美国华盛顿大学的Arka Majumdar教授共同组织。本专题得到了同行的积极响应,共收录了国内外专家学者的11篇高质量论文。专题内容可分为四个部分:
第一部分
关于非线性光学超构表面和拓扑超构表面
1. 来自澳大利亚国立大学的Yuri Kivshar院士等的综述论文:
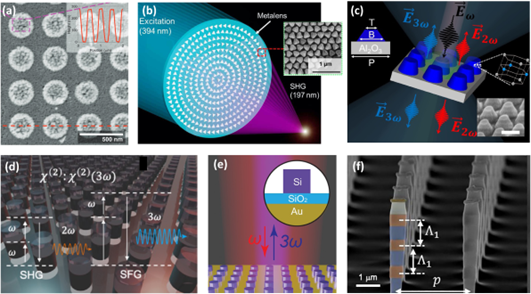
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: Nonlinear optics is a well-established field of research that traditionally relies on the interaction of light with macroscopic nonlinear media over distances significantly greater than the wavelength of light. However, the recently emerged field of optical metasurfaces provides a novel platform for studying nonlinear phenomena in planar geometries. Nonlinear optical metasurfaces introduce new functionalities to the field of nonlinear optics extending them beyond perturbative regimes of harmonic generation and parametric frequency conversion, being driven by mode-matching, resonances, and relaxed phase-matching conditions. Here we review the very recent advances in the rapidly developing field of nonlinear metasurface photonics, emphasizing multi-frequency and cascading effects, asymmetric and chiral frequency conversion, nonperturbative nonlinear regimes, and nonlinear quantum photonics, empowered by the physics of Mie resonances and optical bound states in the continuum.
2. 来自东南大学等单位的崔铁军院士、游检卫教授等的综述论文:
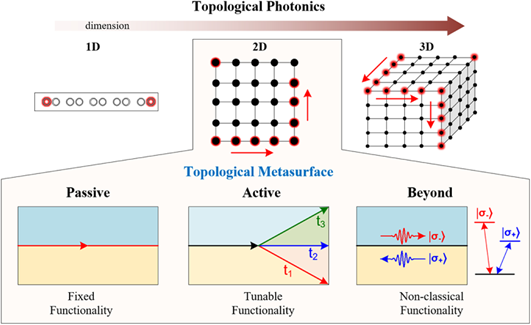
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: Metasurfaces are subwavelength structured thin films consisting of arrays of units that allow the control of polarization, phase, and amplitude of light over a subwavelength thickness. Recent developments in topological photonics have greatly broadened the horizon in designing metasurfaces for novel functional applications. In this review, we summarize recent progress in the research field of topological metasurfaces, first from the perspectives of passive and active in the classical regime, and then in the quantum regime. More specifically, we begin by examining the passive topological phenomena in TWo-dimensional photonic systems, including both time-reversal broken systems and time-reversal preserved systems. Subsequently, we discuss the cutting-edge studies of active topological metasurfaces, including nonlinear topological metasurfaces and reconfigurable topological metasurfaces. After overviewing topological metasurfaces in the classical regime, we show how they could provide a new platform for quantum information and quantum many-body physics. Finally, we conclude and describe some challenges and future directions of this fast-evolving field.
第二部分
纳米加工与先进成像技术
3. 新加坡科技设计大学的Joel Yang 教授等在超构表面的高通量制备方面的进展:
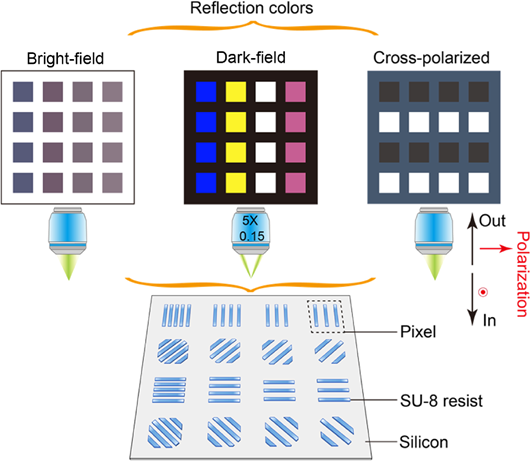
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: The field of metasurface research has rapidly developed in the past decade. Electron-beam lithography (EBL) is an excellent tool used for rapid prototyping of metasurfaces. However, Gaussian-beam EBL generally struggles with low throughput. In conjunction with the recent rise of interest in metasurfaces made of low-index dielectric materials, we propose in this study the use of a relatively unexplored chemically amplified resist, SU-8 with EBL, as a method for rapid prototyping of low-index metasurfaces. We demonstrate the use of SU-8 grating on silicon for cost-efficient fabrication of an all-dielectric multilevel security print for anti-counterfeiting purposes, which encrypt different optical information with different light illumination conditions, namely, bright-field reflection, dark-field reflection, and cross-polarized reflection. The large-scale print (1 mm2) could be exposed in a relatively short time (∼11 min) due to the ultrahigh sensitivity of the resist, while the feature size of ∼200 nm was maintained, demonstrating that SU-8 EBL resist serves as a good candidate for rapid prototyping of metasurface designs. Our results could find applications in the general area of increasing EBL patterning speed for a variety of other devices and structures.
4.中科院光电研究所的罗先刚院士、郭迎辉教授等提出了构建多维无透镜成像的新方法:
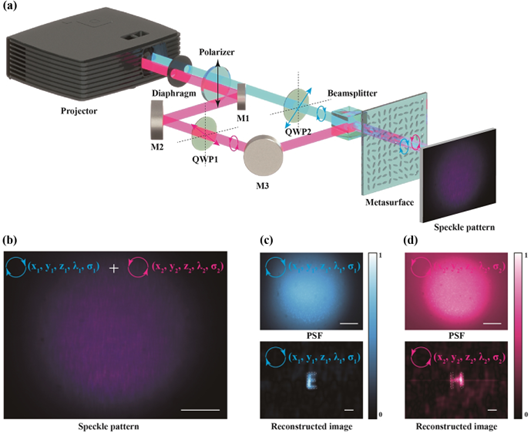
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: Multi-dimensional optical imaging systems that simultaneously gather intensity, depth, polarimetric, and spectral information have numerous applications in medical sciences, robotics, and surveillance. Nevertheless, most current approaches require mechanical moving parts or multiple modulation processes and thus suffer from long acquisition time, high system complexity, or low sampling resolution. Here, a methodology to build snapshot multi-dimensional lensless imaging is proposed by combining planar-optics and computational technology, benefiting from sufficient flexibilities in optical engineering and robust information reconstructions. Specifically, a liquid crystal diffuser based on geometric phase modulation is designed to simultaneously encode the spatial, spectral, and polarization information of an object into a snapshot detected speckle pattern. At the same time, a post-processing algorithm acts as a special decoder to recover the hidden information in the speckle with the independent and unique point spread function related to the position, wavelength, and chirality. With the merits of snapshot acquisition, multi-dimensional perception ability, simple optical configuration, and compact device size, our approach can find broad potential applications in object recognition and classification.
5. 南京大学的李涛教授等基于铌酸锂超构表面实现大了视场的光学相控阵:
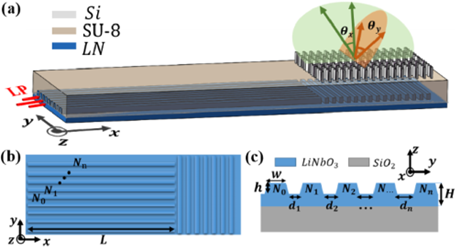
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: Integrated optical phased arrays (OPAs) have attracted significant interest to steer laser beams for applications including free-space communications, holography, and light detection and ranging. Although many methods have been proposed to suppress grating lobes, OPAs have also been limited by the trade-off between field of view (FOV) and beamforming efficiency. Here, we propose a metasurface empowered port-selected OPA (POPA), an OPA steered by port selection, which is implemented by an aperiodic waveguide array with an average pitch less than the wavelength and phase controlled by coupling among waveguides. A metasurface layer above the POPA was designed to increase wide FOV steering, aliasing-free by polarization division. As a result, we experimentally demonstrate beam scanning over a±41.04°×7.06°±41.04°×7.06° FOV. The aliasing-free POPA with expanded FOV shows successful incorporation of the waveguide-based OPA technique with an emerging metasurface design, indicating much exploration in concepts for integrated photonic devices.
6. 韩国浦项科技大学的Junsuk Rho教授和Jong-Lam Lee教授等实现高数值孔径RGB消色差超构透镜:
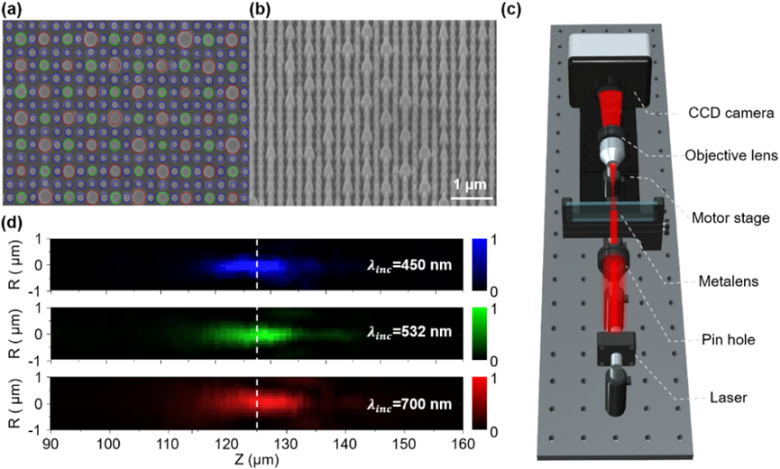
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: We theoretically and experimentally demonstrate an RGB achromatic metalens that operates concurrently at three visible wavelengths (λ=450, 532, and 700 nm) with a high numerical aperture of 0.87. The RGB metalens is designed by simple integration of metalens components with the spatial interleaving method. The simulated spatial interleaving metalens shows RGB achromatic operation with focusing efficiencies of 25.2%, 58.7%, and 66.4% at the wavelengths of 450, 532, and 700 nm, respectively. A 450 μm diameter metalens operating at three designated wavelengths is fabricated with low-loss hydrogenated amorphous silicon. The fabricated metalens has the measured focusing efficiencies of 5.9%, 11.3%, and 13.6% at λ=450, 532, and 700 nm, respectively. The Strehl ratios of 0.89, 0.88, and 0.82 are obtained at given wavelengths, which show a capability of diffraction-limited operation.
第三部分
利用超构表面实现对光场的多维调控
7. 西北工业大学的赵建林教授、李鹏教授等实现了基于光学超构表面干涉仪的自旋光束分束,该文被遴选为PR Optical Metasurfaces: Fundamentals and Applications专题封面(On the Cover)文章:
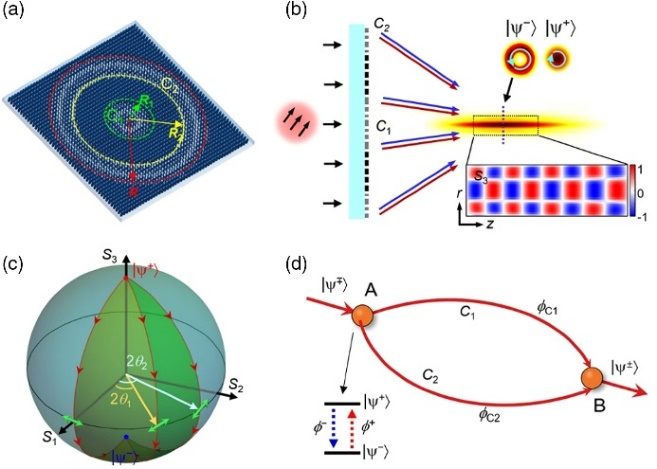
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: Spin splitting of light originates from the interplay between the polarization and spatial degrees of freedom as a fundamental constituent of the emerging spin photonics, providing a prominent pathway for manipulating photon spin and developing exceptional photonic devices. However, previously relevant devices were mainly designed for routing monotonous spin splitting of light. Here, we realize an oscillatory spin splitting of light via metasurface with two channel Pancharatnam–Berry phases. For the incidence of a linearly polarized light, the concomitant phases arising from opposite spin states transition within pathways of the metasurface induce lateral spin splitting of light with alternately changed transport direction during beam guiding. We demonstrate the invariance of this phenomenon with an analogous gauge transformation. This work provides a new insight on steering the photon spin and is expected to explore a novel guiding mechanism of relativistic spinning particles, as well as applications of optical trapping and chirality sorting.
8. 中山大学刘进教授、王雪华教授等基于量子点与超构表面的耦合效应的实现高性能单光子源:
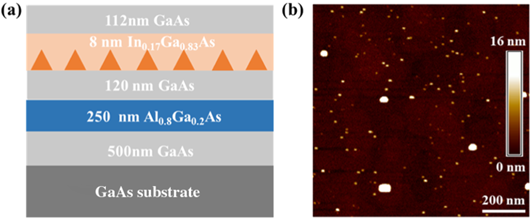
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: High-performance solid-state quantum sources in the telecom band are of paramount importance for long-distance quantum communications and the quantum Internet by taking advantage of a low-loss optical fiber network. Here, we demonstrate bright telecom-wavelength single-photon sources based on In(Ga)As/GaAs quantum dots (QDs) deterministically coupled to hybrid circular Bragg resonators (h-CBRs) by using a wide-field fluorescence imaging technique. The QD emissions are redshifted toward the telecom O-band by using an ultra-low InAs growth rate and an InGaAs strain reducing layer. Single-photon emissions under both continuous wave (CW) and pulsed operations are demonstrated, showing high brightness with count rates of 1.14MHz and 0.34 MHz under saturation powers and single-photon purities of g(2)(0)=0.11±0.02 (CW) and g(2)(0)=0.087±0.003 (pulsed) at low excitation powers. A Purcell factor of 4.2 with a collection efficiency of 11.2%±1%11.2%±1% at the first lens is extracted, suggesting efficient coupling between the QD and h-CBR. Our work contributes to the development of highly efficient single-photon sources in the telecom band for fiber-based quantum communication and future distributed quantum networks.
9. 新加坡南洋理工大学的罗宇教授、苏州大学的李孝峰教授等基于硅超构器件中的时空调制效应实现了级联参量放大过程:
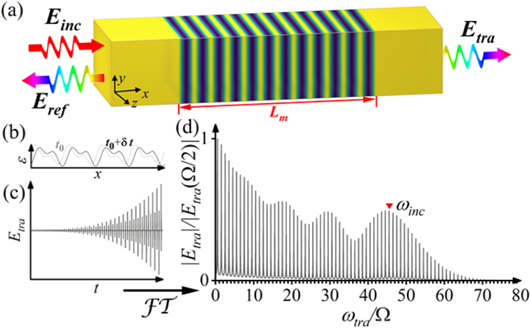
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: Active devices have drawn considerable attention owing to their powerful capabilities to manipulate electromagnetic waves. Fast and periodic modulation of material properties is one of the key obstacles to the practical implementation of active metamaterials and metasurfaces. In this study, to circumvent this limitation, we employ a cascaded phase-matching mechanism to amplify signals through spatiotemporal modulation of permittivity. Our results show that the energy of the amplified fundamental mode can be efficiently transferred to that of the high harmonic components if the spatiotemporal modulation travels at the same speed as the signals. This outstanding benefit enables a low-frequency pump to excite parametric amplification. The realization of cascaded parametric amplification is demonstrated by finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulations and analytical calculations based on the Bloch–Floquet theory. We find that the same lasing state can always be excited by an incidence at different harmonic frequencies. The spectral and temporal responses of the space-time modulated slab strongly depend on the modulation length, modulation strength, and modulation velocity. Furthermore, the cascaded parametric oscillators composed of a cavity formed by photonic crystals are presented. The lasing threshold is significantly reduced by the cavity resonance. Finally, the excitation of cascaded parametric amplification relying on the Si-waveguide platform is demonstrated. We believed that the proposed mechanism provides a promising opportunity for the practical implementation of intense amplification and coherent radiation based on active metamaterials.
第四部分
如何利用先进材料实现新颖的光学调控功能
10. 澳大利亚国立大学的Dragomir N. Neshev教授等探讨基于相变材料的超构表面在光信号调制方面的应用:
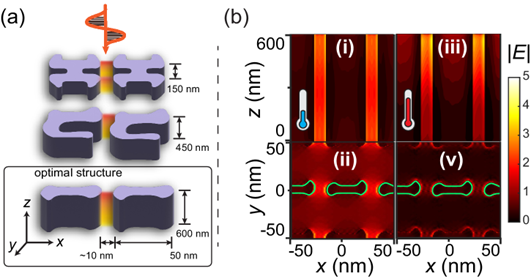
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: Integrated optical phased arrays (OPAs) have attracted significant interest to steer laser beams for applications including free-space communications, holography, and light detection and ranging. Although many methods have been proposed to suppress grating lobes, OPAs have also been limited by the trade-off between field of view (FOV) and beamforming efficiency. Here, we propose a metasurface empowered port-selected OPA (POPA), an OPA steered by port selection, which is implemented by an aperiodic waveguide array with an average pitch less than the wavelength and phase controlled by coupling among waveguides. A metasurface layer above the POPA was designed to increase wide FOV steering, aliasing-free by polarization division. As a result, we experimentally demonstrate beam scanning over a ±41.04°×7.06°±41.04°×7.06° FOV. The aliasing-free POPA with expanded FOV shows successful incorporation of the waveguide-based OPA technique with an emerging metasurface design, indicating much exploration in concepts for integrated photonic devices.
11. 厦门大学陈焕阳教授、新加坡国立大学的仇成伟教授等探讨了如何利用各向异性费马原理调控双曲范德瓦尔斯极化激元:
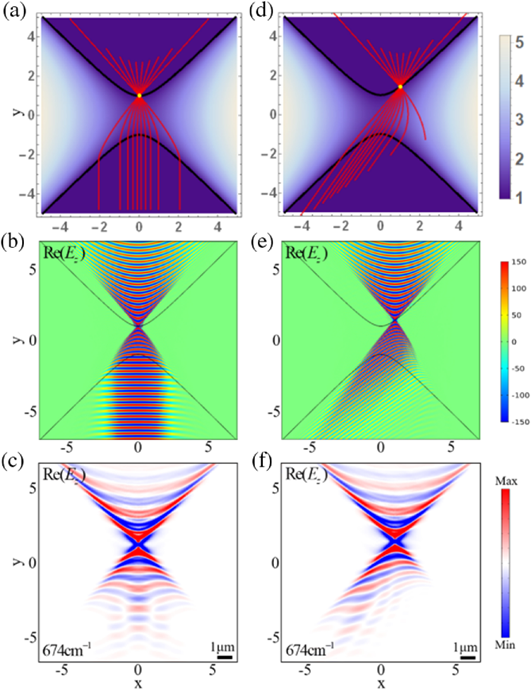
向上滑动阅览
Abstract: Transformation optics (TO) facilitates flexible designs of spatial modulation of optical materials via coordinate transformations, thus, enabling on-demand manipulations of electromagnetic waves. However, the application of TO theory in control of hyperbolic waves remains elusive due to the spatial metric signature transition from (+,+) to (−,+) of a two-dimensional hyperbolic geometry. Here, we proposed a distinct Pythagorean theorem, which leads to establishing an anisotropic Fermat’s principle. It helps to construct anisotropic geometries and is a powerful tool for manipulating hyperbolic waves at the nanoscale and polaritons. Making use of absolute instruments, the excellent collimating and focusing behaviors of naturally in-plane hyperbolic polaritons in van der Waals α–MoO3 layers are demonstrated, which opens up a new way for polaritons manipulation.
专题编辑简介

李贵新,南方科技大学工学院材料科学与工程系教授,Optica Fellow(美国光学学会会士)、香港求是科技基金会2019年杰出青年学者奖获得者。1999-2006毕业于北京师范大学物理系,获理学学士、硕士学位,2009年于香港浸会大学物理系取得博士学位。曾于香港浸会大学、伦敦帝国理工学院、英国伯明翰大学、德国帕德博恩大学等研究机构任博士后、研究助理教授等职。在Nature Photonics, Nature Physics, Nature Reviews Materials, Nature Materials, Nature Nanotechnology, PNAS等期刊发表SCI论文100余篇,引用10000余次。研究工作曾多次被《自然-光子学》、《自然-纳米技术》、《自然-物理》、国际光电工程学会 (SPIE) 作为亮点报道。担任Photonics Research、Advanced Photonics特邀编辑,Advanced Photonics Nexus编委会成员、中国材料研究学会超材料分会常务理事。

Thomas Pertsch,德国耶拿大学阿贝光子中心的董事会成员,应用物理学院院长。他是图林根量子光学与传感创新中心的董事会成员,也是应用物理研究所纳米与量子光学小组的负责人。

肖淑敏,哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)教授。研究团队主要从事基于半导体光学材料和器件的制备,涉及研究内容包括微纳米体系的数值建模、光刻或电子束曝光以及反应离子刻蚀等的微纳米制备技术、以及光学和电学表征技术。近年来在国际刊物和会议上发表相关的优秀原创论文1400余篇,其中Nature 1 篇、 Science 1 篇、 Nature Communications 9篇、Science Advances 1篇、Advanced Materials等高水平论文32篇,合著专著一部,多篇文章单篇他引超过200次。

推荐阅读:
编辑 | 木拉提·满苏尔
免责声明:本文旨在传递更多科研资讯及分享,所有其他媒、网来源均注明出处,如涉及版权问题,请作者第一时间联系我们,我们将协调进行处理,最终解释权归旭为光电所有。







