Chip发表南方科技大学余浩和东南大学崔铁军院士团队长篇综述论文:硅等离子体太赫兹超材料器件
FUTURE | 远见 闵青云 选编
近日,南方科技大学余浩和东南大学崔铁军院士团队以「Terahertz metadevices for silicon plasmonics」¹为题在Chip上发表长篇综述论文,全面深入地回顾和总结了近年来用于硅等离子体的太赫兹超材料器件领域的发展。本文第一作者为梁元,通讯作者为余浩。Chip是全球唯一聚焦芯片类研究的综合性国际期刊,是入选了国家高起点新刊计划的「三类高质量论文」期刊之一。

文章首先介绍了一种用于未来高速服务器互联的等离子体I/O (Plasmonic I/O)通信系统。该系统同时将表面等离子体基元(Spoof Surface Plasmon Polaritons,SSPP)和开环谐振器(Split-Ring Resonator,SRR)集成于片上,并在140 GHz(亚)太赫兹频段进行多信道等离子数据传输。该收发机是首次将多种超材料与互补金属氧化物半导体(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor,CMOS)电路同时集成于硅片上,并进行串扰抑制的多通道通断键控(On-Off Keying,OOK)通信系统。系统架构如图1所示,该系统由多双信道并行组成,每个信道之间数据通信相对独立。发射机(Transmitter,TX)由多个基于SRR幅度调制器和一个信号源组成。TX同时包括一个等离子体的辐射超表面。信号源由四个振荡器耦合并做功率合成,合成后的信号直接驱动多个幅度调制器。接收机(Receiver, RX)由变压器、下变频混频器和基带放大器构成。相比于传统的I/O,例如基带电传输系统,该系统拥有更小的功耗和延迟,以及低串扰的特点。相比于光通信系统,该系统全集成于片上且无需额外的光器件和封装,适用于更多场景并且造价更低。最近研究表明,当合理布局SSPP的设计尺寸时,多通道等离子体I/O能实现1 Gbps μm⁻¹的信道密度²。此外,由于信道间串扰被表面波传输线显著抑制,单通道等离子体I/O的通信速率可达300 Gbps,展现出相比于任何传统通信方式在功耗、速率、面积、延迟和集成度上的优势。该等离子体I/O有潜力成为未来多信道高速太赫兹通信的主流架构之一。
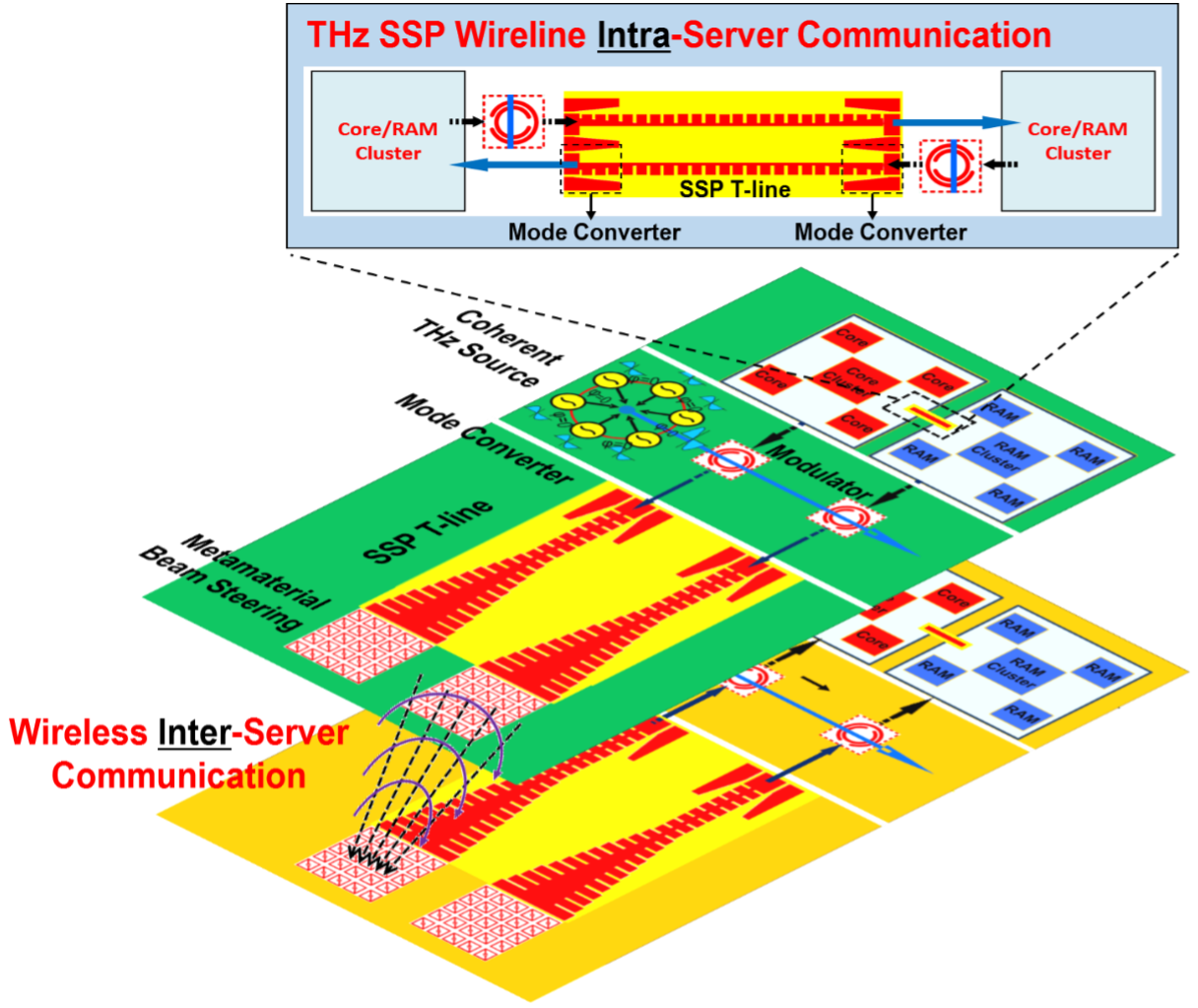
图1 | 基于片上超材料的多通道太赫兹等离子体I/O (Plasmonic I/O)通信系统。
鉴于超材料对于太赫兹I/O系统性能提升的帮助,本文接下来回顾了SSPP和SRR两种超材料在硅基芯片上的发展史和它们在毫米波/太赫兹频段的最新应用。文章介绍了当今超高频段、高速数据通信的发展,并指出硅基全集成芯片在通信领域的瓶颈,例如功耗、信道串扰、发射功率、调制开关比等。随后,文章指出上述难题有可能被集成超材料解决。集成超材料为目前最前沿的研究方向之一,其在毫米波/太赫兹波段独有的物理特性受到广泛关注。然而,目前的科研方向主要集中在独立超材料的设计问题,而鲜有文章讨论超材料与电路的集成以及这种集成对高速通信带来的优势。此文详细介绍了这两种超材料与电路集成的最新进展,并展示等离子体 I/O的性能优势。
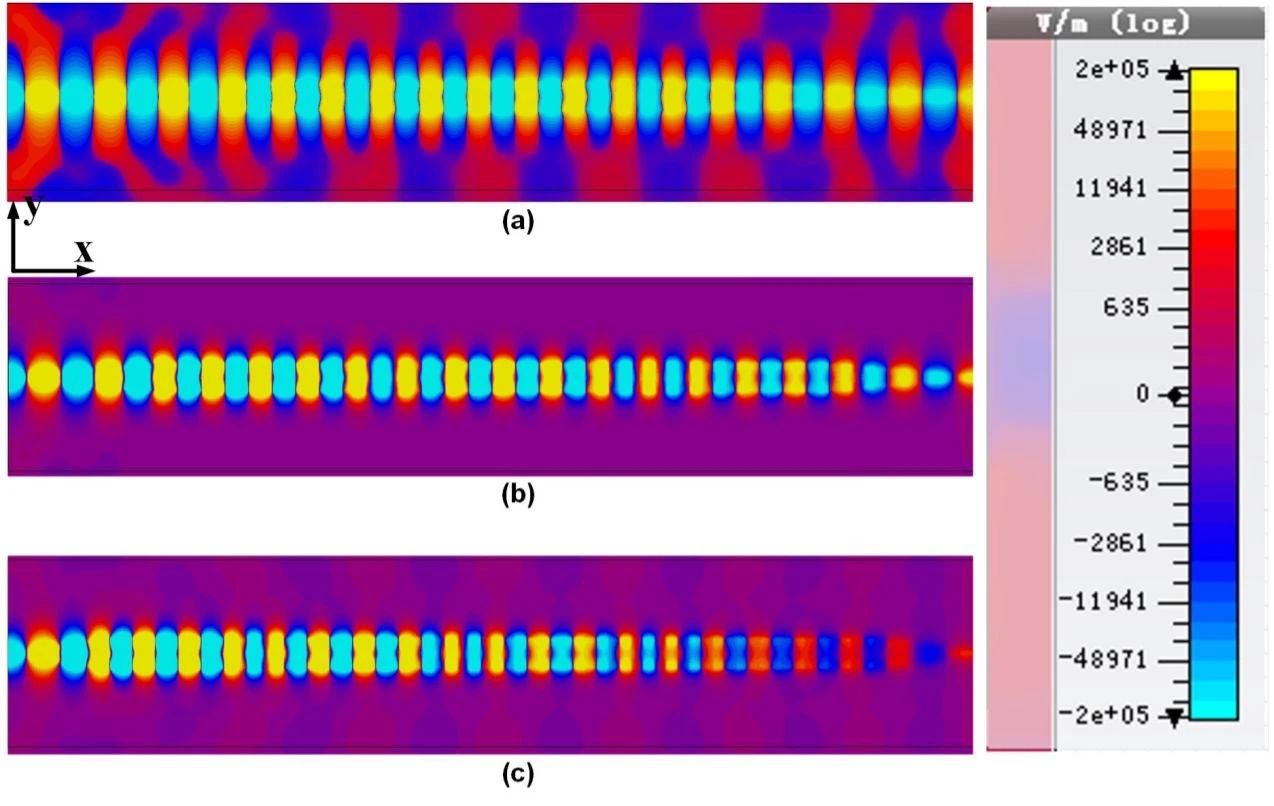
图2 | 片上SSPP模式转换及表面等离子体传输线。
文章介绍了SSPP的物理模型,并给出了相应的数学基础,对SSPP的色散曲线,场束缚的能力进行讨论。随后,文章介绍了近十年SSPP在毫米波/太赫兹频段的运用,还重点介绍了余浩团队近几年在SSPP片上传输线的研究成果²⁻⁴。其中,先介绍了一对紧密放置的并在片上集成的SSPP传输线²,金属间距仅为2.4 𝜇m。受益于SSPP传输线的场束缚特性,与传统片上传输线相比,当通信距离为2毫米时,所设计的SSPP传输线将信道串扰抑制了19 dB (接近100倍)。由此也导致损耗的降低。其次,文章讲述了从传统波导渐变为SSPP传输线的模式转换结构⁴。由图2所示,该结构由渐变的凹槽结构组成,旨在进行动量和阻抗转换。当没有该转换结构时,SSPP传输的反射系数在多个频段大于−5 dB。当使用该转换结构时,反射系数可以降低到−8 dB以下。由此,整体传输损耗也得以降低。
作为另外一种重要的超材料结构,SRR的片内设计/集成也在文中被详细介绍。其在太赫兹波段展现的高品质因子很适合多种片上设计场景,例如振荡器、调制器、信号源等。文章首先回顾了近10年SRR超材料在太赫兹领域的运用,及其实现的优异性能,随后对余浩团队近几年在该领域的成果进行概括。例如,基于SRR结构的幅度调制器⁵,该调制器灵活运用了SRR超材料的特性,具有超高的品质因子,较小的面积以及无静态功耗。与单层SRR相比,在CMOS上堆叠多层SRR可以提升整个SRR谐振器的品质因子。当SRR调制器上的开关断开时,信号被全部反射;当SRR调制器上的开关导通时,信号以低插损通过SRR谐振器,由此实现幅度调制。所测试得到的品质因子高达83,幅度调制开关比为40 dB。与其他在CMOS工艺上集成的无源调制器相比,此设计实现了最高的开关比并占用最小的面积。此外,该设计不消耗静态支流功耗,与传统有源幅度调制器相比能极大降低系统功耗。
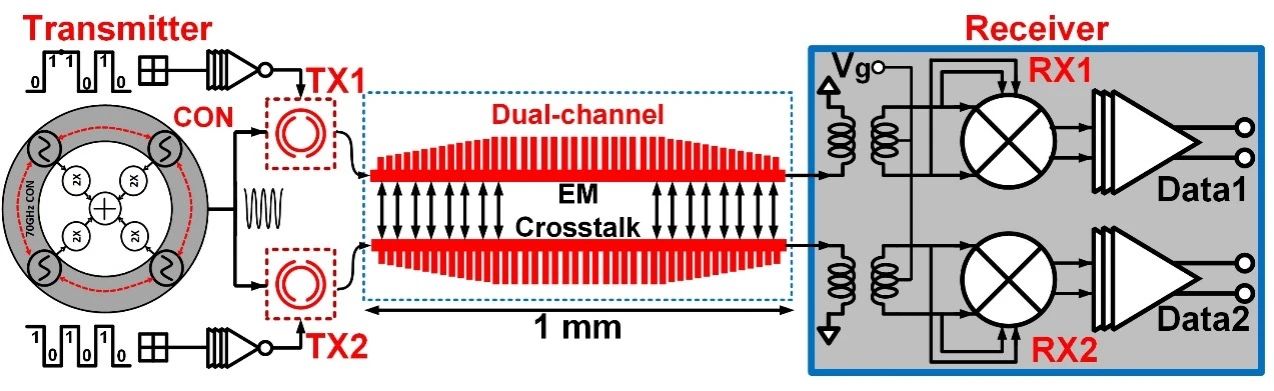
图3 | 基于片上超材料的140 GHz 13.5 Gb s⁻¹双通道太赫兹等离子体I/O (Plasmonic I/O) OOK通信系统。
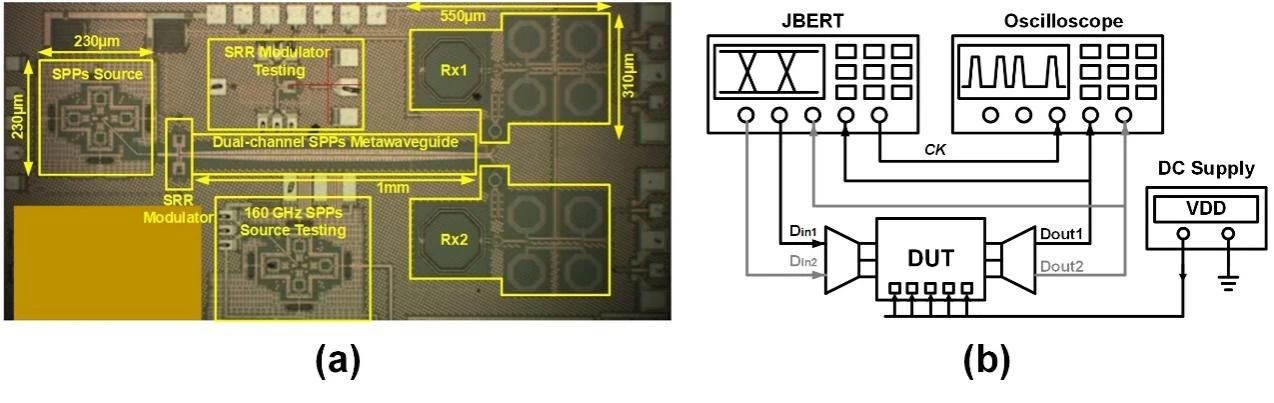
图4 | (a)140 GHz Plasmonic I/O芯片版图,(b)测试方法。
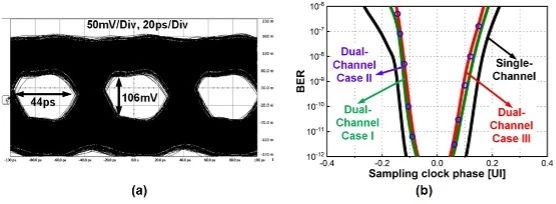
图5 | (a)等离子体I/O测试眼图,(b)测试误码率。
文章还提到了一款基于65 nm工艺的全集成140 GHz 等离子体 I/O⁵,重点阐述了该等离子体I/O的设计初衷、遇到的瓶颈、解决的问题、设计方法和性能优化等。其设计、芯片版图、测试方法及设备分别如图3、图4(a)、图4(b)所示。该收发机同时集成了SSPP和SRR两种超材料,以及太赫兹收发机。所采用的SSPP传输线有效降低信道间串扰超过19 dB,使得密集多通道太赫兹低串扰数据通信成为可能。一对SRR调制器由一个功率合成信号源驱动,在保证链路预算的前提下极大地降低了发射机的功耗。测试结果展现出实现了双通道13.5 Gb /s/lane的通信速度, 10⁻¹²的误码率,以及2.6 pJ bit⁻¹的能效比。图5(a)为双通道同时打开时的测试眼图,图5(b)为测试得到的误码率。综上所述,低串扰、低功耗等特点使得超材料电路展示出优异的性能和替代当前通信系统架构的潜力。基于上述讨论,本文提出了一些潜在的科研方向。
Terahertz metadevices for silicon plasmonics
This article¹ principally reviews a sub-terahertz plasmonic I/O transceiver integrating on-chip spoof surface plasmon polariton (SSP) and split-ring resonator (SRR), which serves as a potential candidate for energy-efficient and high-speed interconnects in future high performance data servers. It was a first-time demonstration of a plasmonic I/O transceiver (TRX) integrating multiple metamaterial devices with CMOS circuit toward crosstalk-immune multi-channel on-off keying (OOK) communication. Compared with traditional I/O, such as baseband signaling, the proposed I/O has reduced power consumption, delay, and electromagnetic crosstalk. Compared with optical interconnects, the proposed I/O can integrate all components in silicon, without the need for extra fabrication processes, optical devices, or relevant packaging. According to a recent study, for transmission length reaching 10 mm, which is approximately the state-of-the-art chip edge length, bandwidth density of ~1 Gb μm⁻¹ can be achieved by choosing an optimal geometrical design for the SSPP metawaveguide². Moreover, the data rate can reach 300 Gbps per channel while the channel crosstalk is significantly suppressed. All these studies show the advantages of plasmonic I/O in terms of energy efficiency, data rate, area, delay, and integration density. Such a plasmonic I/O shows high potential to become one of the mainstream system configurations for designing future high-density integrated THz communication system.
Meanwhile, this article also reviews recent progress in TWo functional metamaterials integrated on silicon chips and their latest applications in the mm wave/THz domains. Two metamaterials, including spoof surface plasmon polaritons (SSPP) and split-ring resonator (SRR), are discussed. The paper points out the bottlenecks of silicon-based fully integrated communication chips, such as power consumption, channel crosstalk, transmitted power, modulation extinction ratio, etc. Fortunately, the above challenges may be addressed by integrated metamaterials.
Integrated metamaterials have attracted much recent attention due to their unique physical properties, particularly in the mm-wave/THz regime. However, current research efforts mainly focus on the on-chip design of independent metamaterials, and only a few articles investigated the integration of metamaterials with CMOS circuits, as well as the possible merits offered by such integration. This article recounts the recent advances and performance advantages of several fully integrated metamaterials-based integrated circuit systems.
Additionally, the physical model of SSPP is also reviewed, along with its mathematical basis, its properties and applications. This article also presents the research works of Prof. Hao Yu’s group on silicon-based SSPP transmission lines in recent years²⁻⁴.
As another important metamaterial structure, SRR is discussed in detail. The high quality factor of SRR in the THz domain affords it high potential in various design scenarios such as oscillators, modulators, signal sources, etc. This paper reviews the fundamentals of SRR metamaterial, and then its application to recent THz designs. The extraordinary performance of SRR metamaterials has been revealed, including low radiation loss, small footprint, high absorption, field enhancement, reconfigurability, etc. In particular, an SRR-based modulator⁵ is highlighted. The proposed modulator exhibits high quality-factor resonance and small size, while it consumes no static power. It achieved a measured quality factor of 83, and an extinction ratio of 40 dB. Compared with state-of-the-art on-chip passive modulator, the proposed design achieved the highest extinction ratio, while occupying the smallest area. Moreover, it enables the design of low power transmitters at THz.
Finally, a fully integrated metamaterials-based 140 GHz 13.5 Gb s⁻¹ plasmonic I/O transceiver implemented in a 65 nm CMOS process is discussed⁵. The transceiver integrates both SSPP and SRR metamaterials, combined with terahertz circuits. The design motivation, bottleneck, as well as the design method, performance optimization, etc., are presented. The reported transceiver demonstrates extraordinary performance such as low power consumption, crosstalk-immune capability, etc., paving a new way for future implementation of energy-efficient multi-lane crosstalk-immune communication system and potentially replacing the existing communication system architectures. Some potential research directions are envisioned at the end.
参考文献:
[1] Liang, Y., Yu, H., Wang, H., Zhang, H. C. & Cui, T. J. Metadevices terahertz for silicon plasmonics. Chip 1, 100030 (2022). [2] Joy, S. R., Erementchouk, M., Yu, H. & P. Mazumder. Spoof plasmon interconnects-communications beyond RC limit. IEEE Trans Commun 67, 599–610 (2019). [3] Liang, Y., Yu, H., Feng, G. Y., Apriyana, A. A. A., Fu, X. J. & Cui, T. J. An energy-efficient and low-crosstalk sub-THz I/O by surface plasmonic polariton interconnect in CMOS. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 65, 2762 (2017). [4] Liang, Y., Yu, H., Zhang, H. C., Yang, C. & Cui, T. J. On-chip sub-terahertz surface plasmon polariton transmission lines in CMOS. Sci. Rep. 5, 14853–14853 (2015). [5] Liang, Y., Boon, C. C., Zhang, H. C., Tang, X.-L., Zhang, Q. & Yu, H. A 13.5-Gb/s 140-GHz silicon redriver exploiting metadevices for short-range OOK communications. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 70, 239–253 (2022).论文链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2709472322000284
免责声明:本文旨在传递更多科研资讯及分享,所有其他媒、网来源均注明出处,如涉及版权问题,请作者第一时间联系我们,我们将协调进行处理,最终解释权归旭为光电所有。