超快成像:基于复数神经网络重构实空间复杂结构
在超快时间尺度上,收集晶体材料的相干衍射图案,通过相位恢复,可对其纳米尺度的晶畴结构进行成像。外延晶体薄膜生长过程中,由于外延失配,会自发形成畴结构。由于薄膜中的晶畴和晶界的散射作用,其相应的面内电阻率会受到一定影响。在超快时间尺度上,通过布拉格相干X射线衍射,观察晶畴和晶界的动力学,对理解薄膜如电输运和应力等特性提供重要线索。在X射线相干衍射成像中,相位恢复一直是一个具有计算挑战的任务。特别地,对于超快时间尺度的成像,单次实验将会有海量的实验数据。
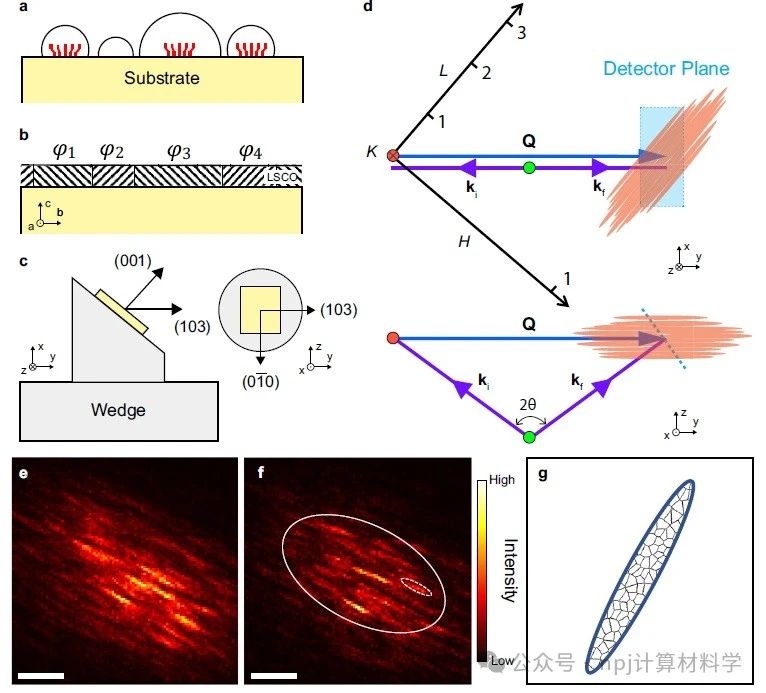
Fig. 1 Domain structure expected due to misfit beTWeen a thin film and its substrate.
近期,来自美国布鲁克海文国家实验室的Xi Yu,Longlong Wu和Ian Robinson等,为研究外延La2-xSrxCuO4(LSCO)薄膜中观察到的异常的电输运特性,该团队使用自由电子激光器(XFEL),对该LSCO薄膜进行了超快布拉格相干衍射成像研究。为解决XFEL实验中相干衍射数据的相位恢复问题,该团队提出了一种新颖的基于复数卷积神经网络的相位恢复方法。这一方法改进了实数卷积神经网络,将复数运算融入卷积计算,从而考虑到了幅值和相位之间的关系。在仿真数据和真实实验数据上,相对于传统的实数卷积神经网络,复数卷积神经网络均展现出更优真实空间复杂结构的重构效果。

相比较于传统实数卷积神经网络,复数卷积神经网络有以下两点不同之处:1. 在神经网络结构上,实数网络输入是测量空间的强度,其输出网络包含两个分支分别输出强度和相位。复数网络的输入和输出都是单一分支,其输入输出都为复数。2. 实数网络的强度分支和相位分支是独立的互不影响的,因此忽视实部和虚部的联系。而复数网络其内部计算则是严格按照复数运算进行,充分考虑了样品的实部和虚部的联系。

Fig. 3 Representative results for the C-CNN and R-CNN for simulated test sets with different number of domains and domain structure.
为了验证所提出的复数模型在相位恢复问题上适用性和鲁棒性。基于监督学习,根据XFEL实验条件,该团队首先将复数神经网络模型应用于拟合数据。通过与传统的实数神经网络模型进行对比,发现所提出的复数神经网络模型能够更好的重构相应的是空间样品信息。由于实验数据通常都存在不同程度的噪声,将该复数神经网络进一步应用于不同信噪比的拟合数据,发现其具有很好的鲁棒性。最终,通过分类处理XFEL数据,应用该复数神经网络模型到应用XFEL所测量的超快布拉格相干衍射数据流上。在超快时间尺度,实验上观察到了相应的晶畴结构及变化。

该工作提出了一种复数卷积神经网络用于解决X射线相干衍射成像中的相位恢复问题。为今后,研究超快相干衍射实验的相位恢复问题中提供了一种新思路。可广泛应用于各类超快相干衍射实验的成像问题上,如全息成像和以及其他外延薄膜应力分布研究等。相关论文近期发布于npj Computational Materials 10: 24 (2024)。手机阅读原文,请点击本文底部左下角“阅读原文”,进入后亦可下载全文PDF文件。

Editorial Summary
During thin film growth, domain wall structures spontaneously form due to epitaxial mismatch. Observingthe dynamics of domains and domain walls at ultrafast timescales can provide fundamental clues for understanding important characteristics that affect electron transport in electronic devices. Thought phase retrieval, single-shot coherent X-ray diffraction patterns allows the imaging of nanoscale domain and domain wall structures. However, phase retrieval, a long-standing computational challenge, involves reconstructing complex-valued image from measured coherent diffraction pattern, which is fundamental in many coherent imaging techniques such as holography, and ptychography.
Xi Yu et.al., from Brookhaven National Laboratory proposed a novel phase retrieval method based on complex-valued convolutional neural networks (C-CNN). This method improves upon traditional real-valued convolutional neural networks by incorporating complex operations into convolutional calculations, thereby considering the relationship between amplitude and phase. On simulated data and real experimental data, the complex-valued CNN demonstrated superior reconstruction performance for complex structures in real space compared to traditional real-valued CNNs.As the C-CNN model can deal with large amounts of coherent diffraction patterns simultaneously, it will benefit experiments where large amounts of data are generated from the same experiments, for example, XFEL experiments. The proposed C-CNN model will be critical to the coherent imaging technique, especially in the case that the conventional method fails. The demonstrated reconstruction method is general for all epitaxial thin-film systems and can be widely applied to coherent diffraction experiments using other sources, so long as they are stable over the exposure time. This article was recently published in npj Computational Materials 10: 24 (2024).
原文Abstract及其翻译
Ultrafast Bragg coherent diffraction imaging of epitaxial thin films using deep complex-valued neural networks (基于复数卷积神经网络的外延薄膜超快布拉格相干衍射成像)
Abstract Domain wall structures form spontaneously due to epitaxial misfit during thin film growth. Imaging the dynamics of domains and domain walls at ultrafast timescales can provide fundamental clues to features that impact electrical transport in electronic devices. Recently, deep learning based methods showed promising phase retrieval (PR) performance, allowing intensity-only measurements to be transformed into snapshot real space images. While the Fourier imaging model involves complex-valued quantities, most existing deep learning based methods solve the PR problem with real-valued based models, where the connection between amplitude and phase is ignored. To this end, we involve complex numbers operation in the neural network to preserve the amplitude and phase connection. Therefore, we employ the complex-valued neural network for solving the PR problem and evaluate it on Bragg coherent diffraction data streams collected from an epitaxial La2-xSrxCuO4 (LSCO) thin film using an X-ray Free Electron Laser (XFEL). Our proposed complex-valued neural network based approach outperforms the traditional real-valued neural network methods in both supervised and unsupervised learning manner. Phase domains are also observed from the LSCO thin film at an ultrafast timescale using the complex-valued neural network.
摘要 外延薄膜生长过程中,随着薄膜厚度增加,由于失配位错,会自发形成畴壁结构。在超快时间尺度上,观察畴和畴壁的动力学可为理解相应电子器件输运等特性提供基本线索。最近,在解决相位恢复问题上,基于深度学习的方法展现出不错的效果。其可将仅有强度信息的倒空间相干衍射图像快速转换为实空间样品信息。尽管在相位恢复时,重构过程涉及到复数变量,但是目前基于深度学习的相位恢复方法主要使用基于实数值的模型来解决相位恢复问题,忽略了样品振幅和相位之间的联系。因此,为在重构过程中保留幅值和相位之间的联系,我们采用复数神经网络来解决相应的相位恢复问题。基于应用X射线自由电子激光器所测量的外延La2-xSrxCuO4(LSCO)薄膜的超快布拉格相干衍射信号,对该神经网络进行评估。所提出的基于复数运算的神经网络,在相位恢复时,无论是对于监督学习,还是非监督学习,其表现均优于传统神经网络。同时使用该神经网络,在超快时间尺度上,我们观察到了LSCO薄膜中的畴结构。
免责声明:本文旨在传递更多科研资讯及分享,所有其他媒、网来源均注明出处,如涉及版权问题,请作者第一时间联系我们,我们将协调进行处理,最终解释权归旭为光电所有。





